Case study – Reformulation project
Pouchitis is the most frequent complication of ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA). In Europe and the United States, the condition is estimated to affect the lives of respectively 150.000 and 80.000 patients.
In collaboration with the Department of Gastroenterology of the University of Leuven, Avivia BV has developed a modified release formulation of metronidazole (MRZ) for the treatment of pouchitis. This formulation aims for a lower systemic and higher local exposure to MRZ, with non-inferior efficacy to standard of care MRZ immediate release (IR) yet at a lower dose making for a more effective treatment with decreased treatment burden, increased quality of life for patients and the potential for chronic or repeated treatment episodes.
The socio-economic impact is related to the avoidance of expensive and burdensome additional surgery and treatments (e.g. biologics) as well as a reduced evolution to chronicity.
Orphan drug designation of MRZ for pouchitis has been granted by the FDA and the COMP.

Case Study – Evolution towards fixed dose combination therapy
Artemisinin based monotherapy, a therapy using one active compound, has been extensively used in Asia and Africa in the ongoing battle against Malaria. A short treatment course of 5 days is sufficient to cure a patient but reoccurrence in this case is fairly common. In order to avoid risk of drug resistance, the WHO recommended to develop Fixed dose combination therapies whereby Artemisinin compounds are combined with other drugs with different modes of action.

Case study CMC development
In the field of complex formulations we have recently worked on nano-emulsions, pH-modified release dosage forms, hydrogels, solid dispersions, melt extrusion, 3-D printed tablets, a four component medicinal product, switching an injectable into a sublingual tablet, solving stability problems of IV solutions, improving bioavailability and solubility of particular drugs, failing bioavailability studies, taste masking in oral formulations, etc. .

Case study Dissolution development: drug vs hypromellose release
The specific analytical methodologies from the Avivia excipient expertise center Excipia allows us to determine not only drug release, but also other relevant drug product characteristics, such as, for example, hypromellose (HPMC) release from a controlled release hypromellose matrix tablets.
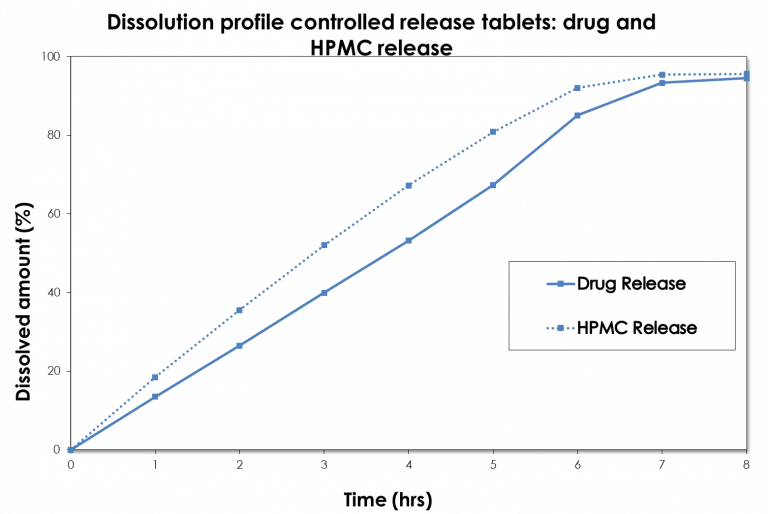
In this particular case, drug and HPMC release was monitored with the USP apparatus III (BioDis). The HPMC release was found to be faster than that of the drug itself; the release mechanism was primarily controlled by erosion. The diffusion-controlled release mechanism was almost absent, making the pharmaceutical formulation extremely sensitive to the HPMC properties. These properties were investigated extensively experts of Excipia and subsequently controlled by defining in-house specifications. Read more.



